Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 State Key Laboratory of Modern Optical Instrumentation, College of Optical Science and Engineering, Zhejiang University, Hangzhou 310027, China
2 Institute for Advanced Interdisciplinary Research, Nanjing University of Aeronautics and Astronautics, Nanjing 210016, China
3 School of Physics and Electronic Science, Hunan University of Science and Technology, Xiangtan 411201, China
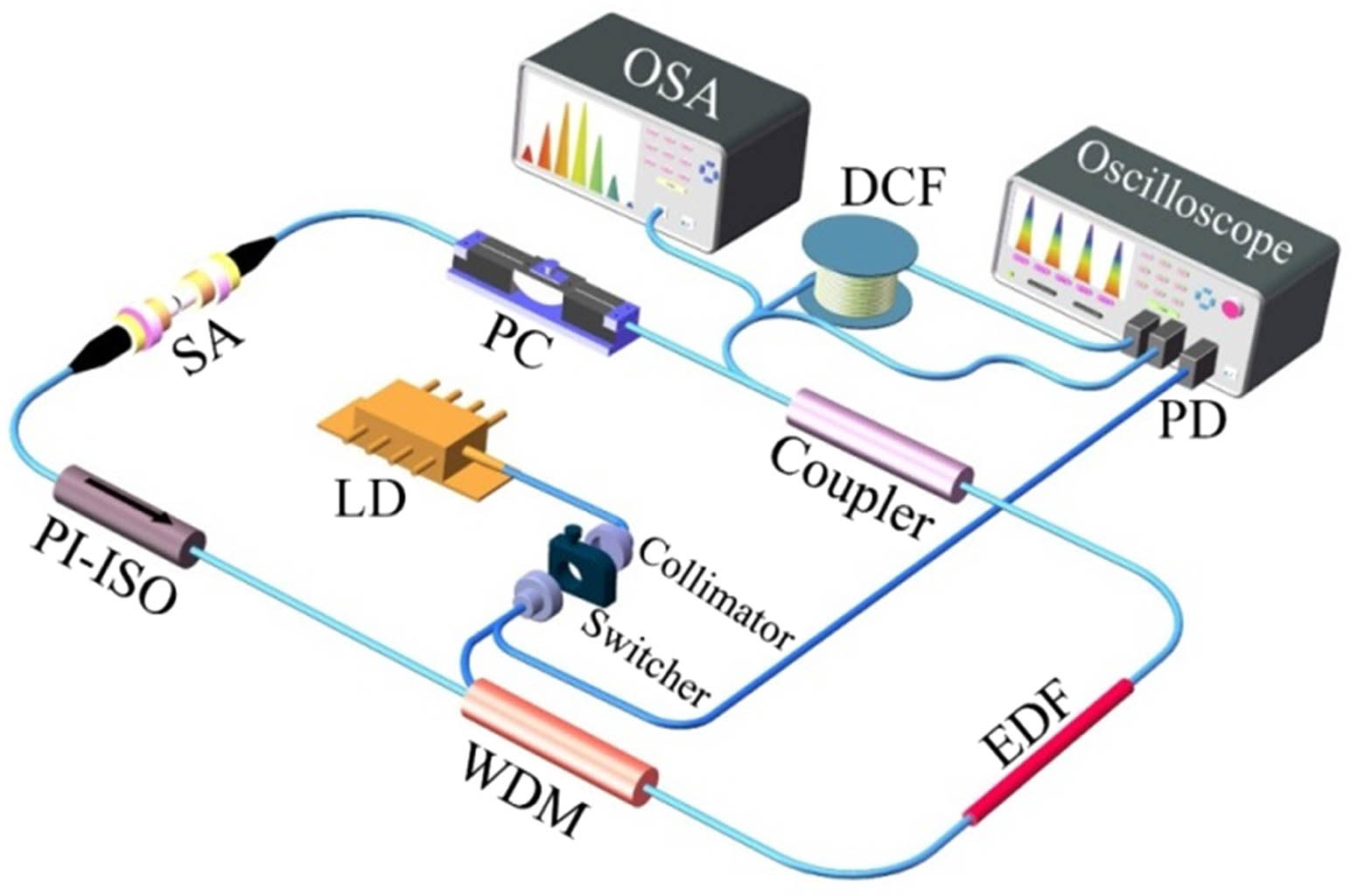
The dispersive Fourier transform (DFT) technique opens a fascinating pathway to explore ultrafast non-repetitive events and has been employed to study the build-up process of mode-locked lasers. However, the shutting process for the mode-locked fiber laser seems to be beyond the scope of researchers, and the starting dynamics under near-zero dispersion remains unclear. Here, the complete evolution dynamics (from birth to extinction) of the conventional soliton (CS), stretched pulse (SP), and dissipative soliton (DS) are investigated by using the DFT technique. CS, SP, and DS fiber lasers mode locked by single-walled carbon nanotubes (SWNTs) are implemented via engineering the intracavity dispersion map. The relaxation oscillation can always be observed before the formation of stable pulse operation due to the inherent advantage of SWNT, but it exhibits distinct evolution dynamics in the starting and shutting processes. The shutting processes are dependent on the dispersion condition and turn-off time, which is against common sense. Some critical phenomena are also observed, including transient complex spectrum broadening and frequency-shift interaction of SPs and picosecond pulses. These results will further deepen understanding of the mode-locked fiber laser from a real-time point of view and are helpful for laser design and applications.
Photonics Research
2019, 7(4): 04000423

Author Affiliations
Abstract
State Key Laboratory of Modern Optical Instrumentation, Department of Optical Engineering, Zhejiang University, Hangzhou 310027, China
The ultrafast fiber laser has attracted a great deal of research interest due to its low cost, high efficiency, and simple maintenance. Optical passive devices are vital parts of a fiber laser. In order to obtain a fiber laser with high quality, optical passive devices with high performance are required. Here, we demonstrate a highly integrated optical device with the combination of a saturable absorber (SA), coupler, isolator, wavelength division multiplexer, and erbium-doped fiber. The built-in SA has a modulation depth of 7% and can withstand high pump power due to the unique structure of the proposed device. The proposed device is applied to an ultracompact fiber laser, which greatly simplifies the laser structure and reduces the size of the proposed laser. The central wavelength, pulse duration, repetition rate, and signal-to-noise ratio of the output soliton are 1560 nm, 1.06 ps, 25.8 MHz, and 50 dB, respectively. The proposed device has great potential for application in high-power and high-frequency fiber lasers. The proposed ultracompact fiber laser has important applications in optical communication, optical sensing, optical frequency combs, and micromachining.
Photonics Research
2019, 7(1): 01000036

Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 Zhejiang University, College of Optical Science and Engineering, State Key Laboratory of Modern Optical Instrumentation, Hangzhou, China
2 Nanjing University of Aeronautics and Astronautics, Institute for Advanced Interdisciplinary Research, Nanjing, China
3 Hunan University of Science and Technology, School of Physics and Electronic Science, Xiangtan, China
Real-time spectroscopy based on an emerging time-stretch technique can map the spectral information of optical waves into the time domain, opening several fascinating explorations of nonlinear dynamics in mode-locked lasers. However, the self-starting process of mode-locked lasers is quite sensitive to environmental perturbation, which causes the transient behaviors of lasers to deviate from the true buildup process of solitons. We optimize the laser system to improve its stability, which suppresses the Q-switched lasing induced by environmental perturbation. We, therefore, demonstrate the first observation of the entire buildup process of solitons in a mode-locked laser, revealing two possible pathways to generate the temporal solitons. One pathway includes the dynamics of raised relaxation oscillation, quasimode-locking stage, spectral beating behavior, and finally the stable single-soliton mode-locking. The other pathway contains, however, an extra transient bound-state stage before the final single-pulse mode-locking operation. Moreover, we propose a theoretical model to predict the buildup time of solitons, which agrees well with the experimental results. Our findings can bring real-time insights into ultrafast fiber laser design and optimization, as well as promote the application of fiber laser.
fiber laser mode-locking self-starting process relaxation oscillation real-time spectroscopy Advanced Photonics
2019, 1(1): 016003

Author Affiliations
Abstract
State Key Laboratory of Modern Optical Instrumentation, Department of Optical Engineering, Zhejiang University, Hangzhou 310027, China
We investigate the properties of spatial solitons in the fractional Schr dinger equation (FSE) with parity-time (PT)-symmetric lattice potential supported by the focusing of Kerr nonlinearity. Both one- and two-dimensional solitons can stably propagate in PT-symmetric lattices under noise perturbations. The domains of stability for both one- and two-dimensional solitons strongly depend on the gain/loss strength of the lattice. In the spatial domain, the solitons are rigidly modulated by the lattice potential for the weak diffraction in FSE systems. In the inverse space, due to the periodicity of lattices, the spectra of solitons experience sharp peaks when the values of wavenumbers are even. The transverse power flows induced by the imaginary part of the lattice are also investigated, which can preserve the internal energy balances within the solitons.
Spatial solitons Fractional Fourier transforms Kerr effect Photonics Research
2018, 6(9): 09000875

Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 Key Lab of Optoelectronic Technology & Systems of Ministry of Education, Chongqing University, Chongqing 400044, China
2 5011 District Measurement Station of Weapon Industry, Chongqing 400050, China
Reflective fiber optic sensors have advantages for surface roughness measurements of some special workpieces, but their measuring precision and efficiency need to be improved further. A least-squares support vector machine (LS-SVM)-based surface roughness prediction model is proposed to estimate the surface roughness, Ra, and the coupled simulated annealing (CSA) and standard simplex (SS) methods are combined for the parameter optimization of the mode. Experiments are conducted to test the performance of the proposed model, and the results show that the range of average relative errors is 4.232%–2.5709%. In comparison with the existing models, the LS-SVM-based model has the best performance in prediction precision, stability, and timesaving.
120.6660 Surface measurements, roughness 060.2370 Fiber optics sensors Chinese Optics Letters
2017, 15(9): 091201
将TEM喇叭天线密封进填充变压器油的尼龙天线罩中, 只要合理设计尼龙天线罩外形, 使变压器油形成聚焦透镜, 不仅能提高天线的功率容量, 还能改善其辐射特性。基于变压器油的缩波效应和椭球的几何性质, 借助几何光学理论, 设计了一款具有聚焦能力的椭球变压器油透镜。变压器油的缩波效应能够增大TEM喇叭天线电尺寸, 使TEM喇叭天线的辐射特性得到初步改善, 透镜的聚焦能力使天线的定向性得到进一步改善。为了验证理论分析的正确性, 另外设计了一款不具有聚焦能力的球状变压器油透镜作为参照, 两款透镜天线仿真结果与理论分析吻合。与大气中的TEM喇叭天线相比, 椭球变压器油透镜使TEM喇叭天线主波束变窄, 远场电压峰峰值提高56.97%, 阻抗带宽低频端从0.28 GHz扩展到0.2 GHz, 功率容量达到18.43 GW。
高功率 TEM喇叭天线 介质透镜 高斯脉冲 几何光学 high power TEM horn antenna dielectric lens Gaussian pulse geometrical optics 强激光与粒子束
2014, 26(8): 083009
1 西南交通大学 电磁研究所, 成都 610031
2 西北核技术研究所, 西安 710024
在时域推导了超宽带脉冲空间功率合成的条件,得到了多路脉冲信号在极化方向相同,幅度、波形一致的条件下,可实现最大化功率输出的结论。基于此提出了一种阵馈的抛物柱反射面天线。采用10喇叭单元叠状排列形成一维馈源阵列放置于焦线上,照射抛物柱反射面后形成相干脉冲,在主轴方向合成超宽带高功率微波波束。仿真结果表明,该阵馈天线较最优口径的单馈源天线,远场辐射功率密度提高了87倍以上,且波束宽度由66°减为8°,实现了超宽带高功率微波的高效空间功率合成。
超宽带 高功率微波 阵馈反射面天线 空间功率合成 ultra-wideband high power microwave array-fed reflector antenna spatial power combination 强激光与粒子束
2014, 26(1): 013005
中国电子科技集团公司第五十五研究所, 南京 210016
为了缩短像增强管系列产品的研发周期,提高产品成品率,结合质量管理的理念提出对像增强管中关键组件的质量控制和检测,并创新地设计和建立了像增强管图像动态测试系统。详细介绍了该系统的结构、功能和特点。该测试系统的使用,能够进一步完善关键组件的质量控制和检测,提高批量生产产品的质量和成品率、降低生产成本外,还能促进提升像管研制水平。
像增强管 动态测试 图像质量 荧光屏 微通道板 image intensifier dynamic test image quality fluorescent screen MCP





